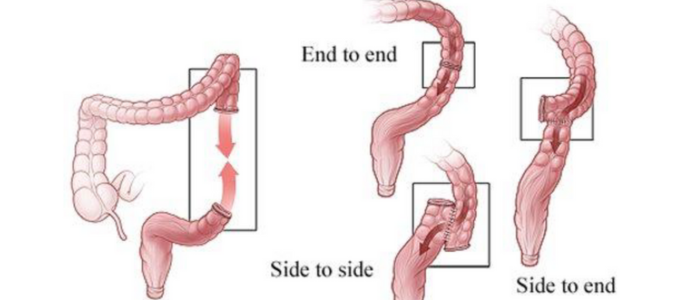
Anastomosis surgically reconnects two ends of a hollow organ, like the intestine, after resection for cancer, obstruction, or inflammatory bowel disease. Symptoms prompting resection include abdominal pain, bleeding, or bowel dysfunction. The procedure, often part of colectomy or rectal resection, can be performed open or laparoscopically, using sutures or staples to join healthy tissue. Risks include leakage, infection, or strictures, which can cause complications like obstruction. Recovery involves a hospital stay and weeks of healing, with dietary adjustments to promote bowel function. Follow-ups monitor for leaks or recurrence of the underlying condition. Anastomosis restores normal digestive flow, improving quality of life. The laparoscopic approach reduces recovery time and pain. Long-term care focuses on maintaining bowel health and preventing complications like adhesions or recurrence.
At the heart of compassionate and expert surgical care stands Dr. Lakshit Tomar, a distinguished Surgical Gastroenterologist dedicated to improving the lives of his patients. With years of experience in advanced wound care, ostomy management, and complex gastrointestinal surgeries, Dr. Tomar blends surgical precision with a deep commitment to patient well-being.
Copyright © 2025 | Powered by [GLS IT Solutions]